Obesity is quickly becoming the most consequential health epidemic in the United States. Obesity is defined as the accumulation of body fat to the point where it becomes detrimental to your health. The effects of obesity on your health are substantial. As an individual's weight increases, so do the risks of developing significant medical issues that can shorten a person's life expectancy. The sad reality is that the disease of obesity directly or indirectly affects every part of our body.
As bariatric professionals, we measure obesity based on your body mass index (BMI). BMI is calculated based on your height and weight. A BMI of 25 to 30 is considered overweight, 30 to 35 is obese, and 35+ is considered morbidly obese.
When a patient's BMI exceeds 30, they are at an increased risk of developing harmful health conditions. These conditions include arthritis, cancers, type 2 diabetes, depression, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obstructive sleep apnea.

Effects of Obesity on Your Health
Obesity is a gateway to all the above-mentioned conditions, leading to a reduced quality of life. The longer you are impacted by obesity, the more these conditions can affect your health. Likewise, the higher your BMI, the more complex these conditions are to control and the more severe they tend to be, potentially leading to coronary artery disease, heart attacks, strokes, and even death.
Treating obesity can add more than ten years to your life expectancy and reduce or cure all of the weight-related conditions associated with your weight. Therefore, it is critical to recognize obesity as a chronic disease and understand how weight gain affects your body.
Effects of Obesity: Arthritis
One pound of weight is equivalent to four pounds of pressure on your joints. As you lose weight, you will experience less pain in your joints due to less pressure. Likewise, your body will decrease cytokine production (inflammatory chemicals released by fat cells), leading to reduced aches and pains.
Effects of Obesity: Diabetes
Patients with excess weight are at a higher risk of being diagnosed with diabetes because they have more fat cells, increasing insulin resistance. This results in the body being incapable of regulating blood sugar levels, ultimately leading to type 2 diabetes.

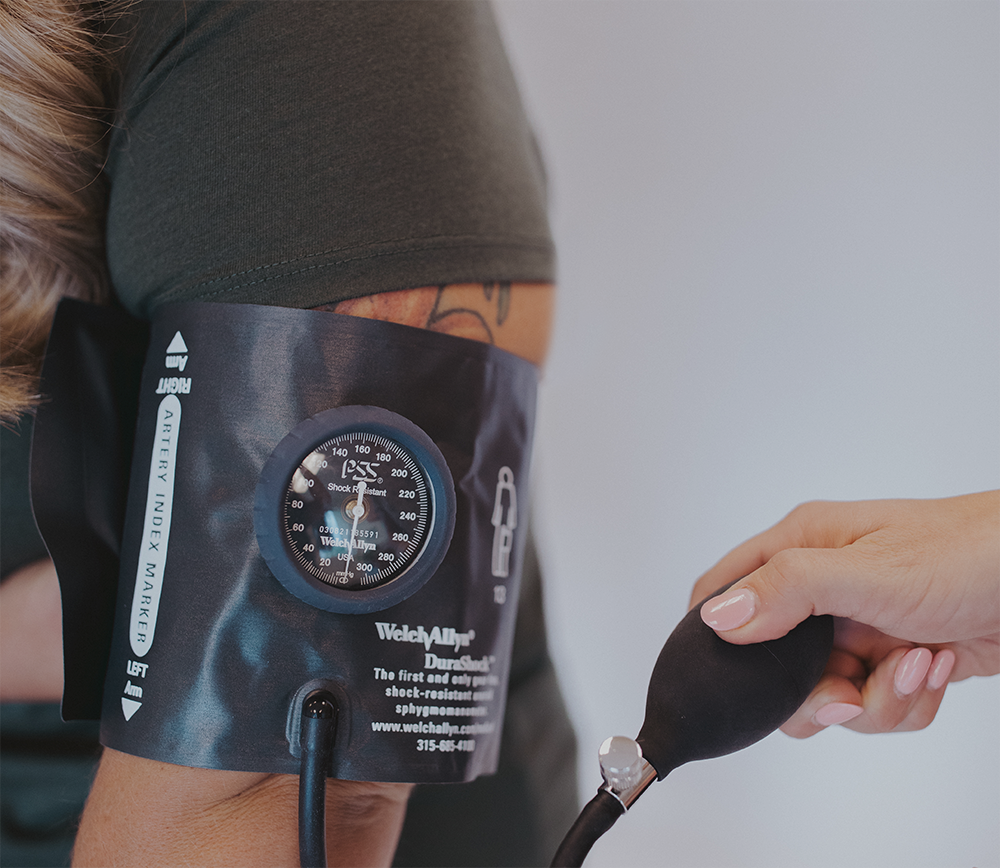
 Impact of Obesity: Hypertension
Impact of Obesity: Hypertension
Studies have found that even a 5% increase in weight can lead to a 30% increase in the risk of developing hypertension. Many theories link obesity and hypertension due to the kidneys not functioning properly since the kidneys play a vital role in filtering the blood. The heavier a person is, the less effective their kidneys are at removing excess waste and liquid from the bloodstream, ultimately leading to the buildup of waste in the body. Similarly, when the kidneys do not function properly, hormones designed to regulate blood pressure are not secreted by this organ.
Impact of Obesity: Heart Disease
Heart disease is commonly associated with cholesterol—a fat-like substance. The liver produces a sustainable amount of cholesterol to help the body encourage new cell and hormone growth. However, cholesterol is also consumed through fatty foods, which can result in plaque buildup in the artery walls over time. As expected, your diet significantly affects your weight; therefore, overweight individuals are at a higher risk of developing heart disease.
Impact of Obesity: Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Patients who are overweight are prone to sleep apnea because the soft tissue in their neck blocks the airway, preventing the patient from breathing. Having sleep apnea can prevent you from losing weight as well. When you have obstructive sleep apnea, you never reach REM sleep and therefore never get a goodnight’s rest. As a result, you are always tired, leading to patients consuming unhealthy food and drinks.
Conclusion
Obesity is a crucial driver of many of the leading causes of death, pain, and suffering in America and worldwide. We highly recommend bariatric surgery for patients struggling with obesity as a treatment option.