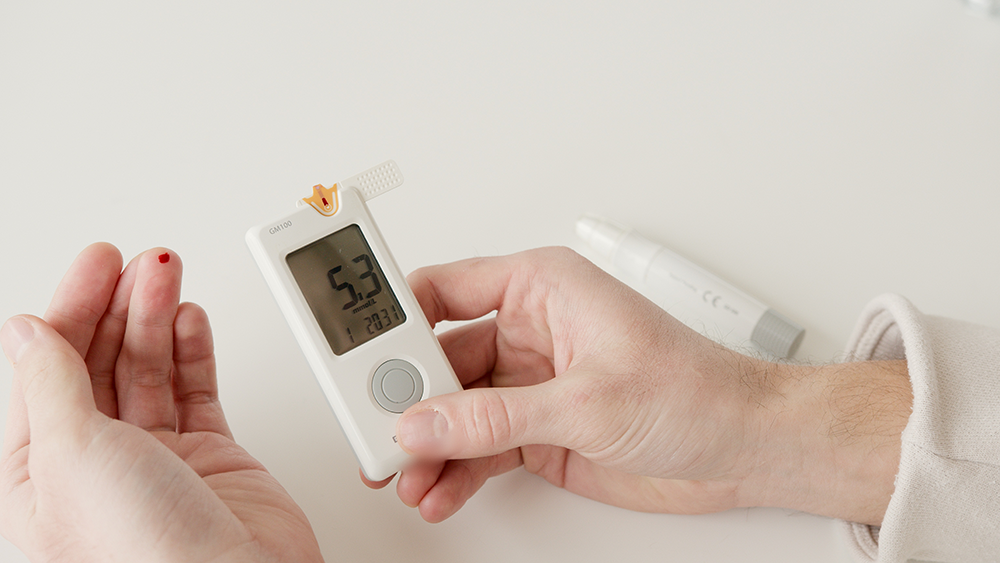
Diabetes has come to be a household term. With the obesity epidemic on the rise, diabetes can be one of the first signs of an unhealthy lifestyle. Diabetes is a disease that is characterized by higher than normal levels of sugar in the blood and not enough insulin to manage these levels
Diabetes: The Definition
Diabetes is a chronic disease that is a result of the pancreas not being able to produce enough insulin or properly regulate insulin levels. Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone that controls the glucose levels in the blood.
In healthy individuals, the sugar and carbohydrates consumed are broken down into glucose, a form of sugar. Glucose is what fuels the body to complete daily tasks; hence why athletes are told to eat a diet high in carbohydrates. However, before the glucose can be used, the cells need insulin to help the body absorb and convert this form of energy to fuel. Insulin also works to lower the blood sugar levels.
In individuals that have diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to convert the glucose into a healthy form of energy. Therefore, over time if the pancreas is not producing enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels, glucose can build up in the blood stream and ultimately lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease and peripheral artery disease if left untreated.
While there are several types of diabetes, the thing they all have in common is higher than normal blood sugar levels. The patients at Live Healthy MD know that too much sugar in the blood acts like poison. It damages the eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, brain and heart.
In fact, if we are calculating your risk of having a heart attack, having diabetes counts toward your risk the same as if you’ve already had a heart attack!
You can calculate your personal risk of having a heart attack if you have the results of your recent cholesterol test
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes:
This is the type that, most of the time, is caused by genetic predisposition. Type 1 diabetes is a result of the immune system mistakenly attacking and killing the cells in the pancreas that trigger the release of insulin, thus minimal amounts of insulin is released into the body. This type of diabetes is treatable by increasing the insulin levels in the bloodstream, i.e. why it is also called "insulin-dependent" diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is fairly rare, only 5-10% of people will be diagnosed with it, and is typically developed during childhood or early adolescence.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is similar to type 1 in that the body does not make enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels, however it can also be characterized by the body not properly using the insulin that is released, i.e. insulin sensitivity. Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults and affects about 90% of the diabetic population.
Most of the time, type 2 diabetes is minimized by weight loss, physical activity, and a healthy lifestyle or in some instances can be treated by medications and insulin.
Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes only occurs in pregnant women and is very uncommon. Due to the change in hormone levels during pregnancy, insulin resistance can result. Gestational diabetes is typically diagnosed during the end of the second or beginning of the third trimester. It is important to control this form of diabetes to ensure the growth and development of the baby.
Prevention Methods:
If diabetes is such a potent risk for heart attack and other life-threatening diseases, what can you do to prevent it?
Almost 90% of all diabetes cases (about 26 million) in the United States are type 2 diabetes and almost 90% of all type 2 diabetics (23.6 million) are overweight or obese, making it the best predictor of who is likely to get diabetes. But there’s good news! By losing only a little bit of weight, you can drastically lower your risk of diabetes. Losing 5% of your body weight lowers your risk of diabetes by almost 50%. If you weigh 200 lbs and lose only 10 lbs, you can cut your risk of diabetes in half.
Both surgical and non-surgical weight loss are important for treating and preventing diabetes. Call today to arrange a consultation with our healthcare providers and see how we focus on diabetes through a focus on weight loss. Until you’re able to see us, you can start today by avoiding processed “white” carbohydrates like noodles, potatoes, rice, bread and grits.